what type of audit event notifies you that an account failed to log on?
Windows Event ID 4625 – Failed logon
- • Introduction
- • Clarification of Event Fields
- • Reasons to monitor
- • The need for a third-political party tool
Introduction
Event ID 4625 (viewed in Windows Event Viewer) documents every failed attempt at logging on to a local reckoner. This event is generated on the computer from where the logon attempt was made. A related consequence, Event ID 4624 documents successful logons.
Event 4625 applies to the following operating systems: Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2016 and Windows x. Corresponding events in Windows Server 2003 and earlier included 529, 530, 531, 532, 533, 534, 535, 536, 537, and 539 for failed logons.
Event ID 4625 looks a little unlike across Windows Server 2008, 2012, and 2016. Highlighted in the screenshots below are the of import fields across each of these versions.
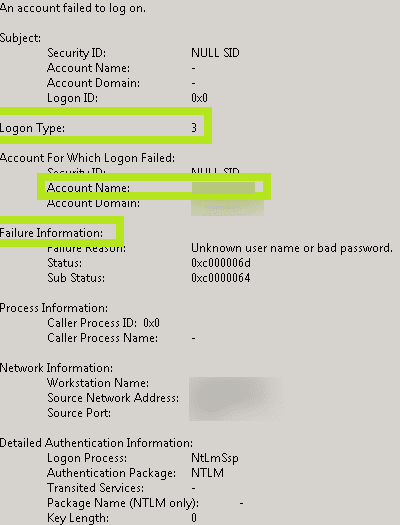
Upshot 4625 (Windows 2008)
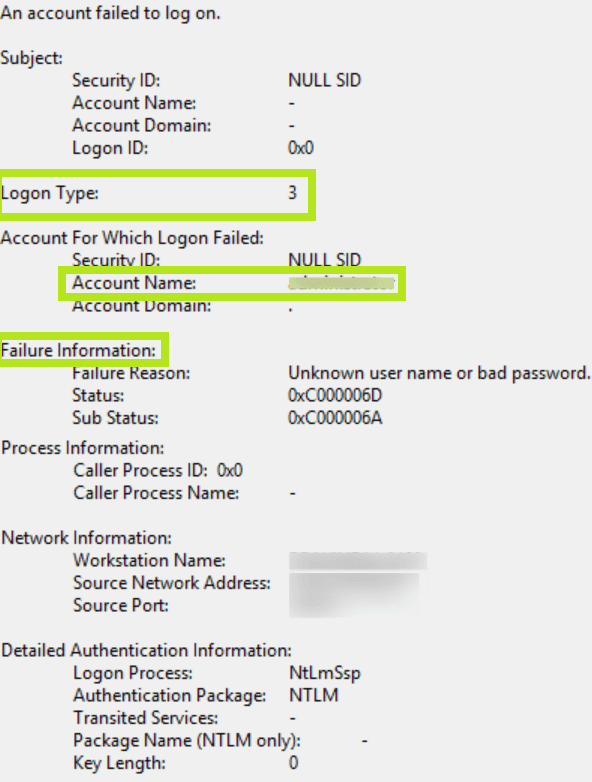
Event 4625 (Windows 2012)
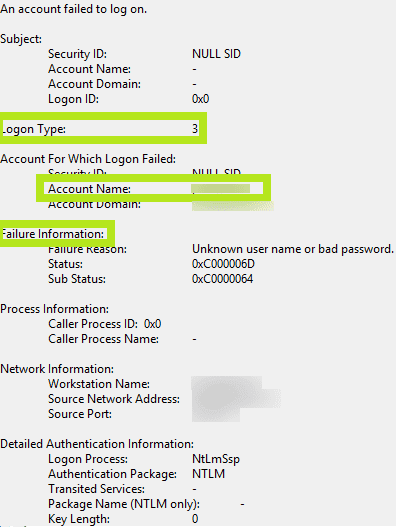
Event 4625 (Windows 2016)
Description of Event Fields
Theimportant information that tin be derived from Effect 4625 includes:
- • Logon Type:This field reveals the kind of logon that was attempted. In other words, it points outhow the user tried logging on. There are a full of ix different types of logons. The most common logon types are: logon type 2 (interactive) and logon type 3 (network). Any logon type other than v (which denotes a service startup) is a red flag. For a description of the different logon types, run across Result ID 4624.
- • Account For Which Logon Failed: This section reveals theAccount Proper noun of the user who attempted the logon.
- • Failure Information: This section explains thereasons for the logon failure. The Failure Reason field includes a short explanation, while the Condition and Sub Status fields list hexadecimal codes, the most common of which are explained beneath.
Status and Sub Condition Codes
Description
0xC0000064
The username is misspelled or does non exist.
0xC000006A
The user'due south password is wrong.
0xC000006D
The username or authentication information is incorrect.
0xC0000234
The user is currently locked out.
0xC0000072
The user account is currently disabled.
0xC000006F
The user tried to log on outside authorized hours.
0xC0000070
The user tried to log on from an unauthorized workstation.
0xC0000193
The user's account has expired.
0xC0000071
The user's password has expired.
0xC0000133
The domain controller and computer's times are out of sync.
0xC0000224
The user is required to change their countersign at next logon.
0xc000015b
The user has not been granted the requested logon type on that machine.
Other data that can be obtained from Event 4625:
- • The Subject section reveals the account on the local organisation that requested the logon (not the user).
- • The Process Information section reveals details surrounding the process that attempted the logon.
- • The Network Information section reveals where the user was when they attempted the logon. If the logon was initiated from your current computer, this data will either be blank or reflect that local figurer's workstation proper name and source network address.
- • The Detailed Authentication section reveals data about the authentication parcel used while attempting the logon.
Reasons to monitor failed logons:
Security
To detectbrute-strength, lexicon, and other password guess attacks, which are characterized by a sudden spike in failed logons.
To detect aberrant and possiblymalicious internal activity, similar a logon attempt from a disabled account or unauthorized workstation, users logging on outside of normal working hours, etc.
Operational
To come up with a benchmark for theAccount lockout threshold policy setting, which determines the number of failed sign-in attempts before a user account gets locked.
Compliance
To comply with regulatory mandates precise data surrounding failed logons is necessary.
The need for a 3rd-party tool
In a typical Information technology environment, the number of events with ID 4625 (failed logon) tin can run into the thousands each twenty-four hour period. Failed logons are useful on their own, just greater insights into network activeness can be fatigued from clear connections between them and other pertinent events.
For instance, while Event 4625 is generated when an account fails to log on and Event 4624 is generated for successful logons, neither of these events reveal if the aforementioned account has recently experienced both. Y'all have to correlate Upshot 4625 with Result 4624 using their respective Logon IDs to figure that out.
Thus,event analysis and correlation needs to be performed. Native tools and PowerShell scripts demand expertise and time when employed to this end, so a third-party tool is truly indispensable.
Applying motorcar learning, ADAudit Plus creates a baseline of normal activities specific to each user and only notifies security personnel when there is a deviation from this norm.
For example, a user who consistently accesses a critical server outside of business hours wouldn't trigger a false positive alert because that behavior is typical for that user. On the other mitt, ADAudit Plus would instantly alert security teams when that aforementioned user accesses that server during a time they've never accessed it earlier, even though the access falls inside business organization hours.
Observe malicious Active Directory logon activity.
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus employs machine learning to alarm y'all whenever a user with perchance malicious intent logs on.
iii of every 5 Fortune 500 companies trust ManageEngine to manage their It.
greenhalghlaregrell.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.manageengine.com/products/active-directory-audit/kb/windows-security-log-event-id-4625.html
0 Response to "what type of audit event notifies you that an account failed to log on?"
Post a Comment